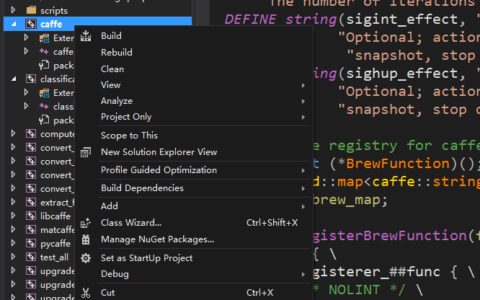
对境准备:对于多个GPU而言,一台机器2个GPU,参数交换的流程图:
参数交换从main()进入train()函数,在train函数中找到对应源码为:
1 . . . . . 2 if (gpus.size() > 1) { 3 caffe::P2PSync<float> sync(solver, NULL, solver->param()); 4 sync.run(gpus); 5 } else { 6 LOG(INFO) << "Starting Optimization"; 7 solver->Solve(); 8 }
因为GPU的个数>1,所以执行sync(solver, NULL, solver->param())和run()函数,首先会执行P2PSync类的构造函数,然后执行run()函数,run函数的代码如下:
1 void P2PSync<Dtype>::run(const vector<int>& gpus) { 2 vector<DevicePair> pairs; 3 DevicePair::compute(gpus, &pairs); 4 SolverParameter param(solver_->param()); 5 vector<shared_ptr<P2PSync<Dtype> > > syncs(gpus.size()); 6 7 // Build the GPU tree by finding the parent for each solver 8 for (int attempts = 0; attempts < pairs.size(); ++attempts) {. . . . . . . 9 } 10 for (int i = 1; i < syncs.size(); ++i) { 11 syncs[i]->StartInternalThread(); 12 } 13 solver_->Solve(); 14 for (int i = 1; i < syncs.size(); ++i) { 15 syncs[i]->StopInternalThread(); 16 } 17 }
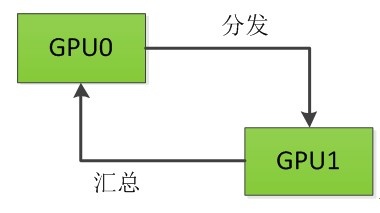
在run()函数中,首先会执行compute()函数,该函数的作用是产生GPU Pairs,GPU Pairs的含义是[parent:child],对于2个GPU而言,GPU Pairs为[-1:0],[0:1],默认根GPU的parent是其本身。然后通过一个for循环构建GPU树,对于2个GPU而言,GPU树如下图所示:
接下来调用一个for循环为每个GPU开启一个线程,值得注意的是for循环是从i=1开始的,即为每个子GPU单独开启一个线程(这里为GPU1开启一个线程),也就是调用StartInternalThread()函数,该函数的代码如下:
1 void InternalThread::StartInternalThread() {. . . . . 2 try { 3 thread_.reset(new boost::thread(&InternalThread::entry, this, device, mode, 4 rand_seed, solver_count, root_solver)); 5 }. . . . . . . 6 }
该函数接着会执行entry()函数,该函数代码如下:
1 void InternalThread::entry(int device, Caffe::Brew mode, int rand_seed, 2 int solver_count, bool root_solver) { 3 . . . . . . 4 InternalThreadEntry(); 5 }
该函数又会去调用InternalThreadEntry()函数,该函数是正式进入迭代运算的入口,代码如下:
1 void P2PSync<Dtype>::InternalThreadEntry() { 2 Caffe::SetDevice(solver_->param().device_id()); 3 CHECK(Caffe::root_solver()); 4 Caffe::set_root_solver(false); 5 // See if there is a defined seed and reset random state if so 6 if (solver_->param().random_seed() >= 0) { 7 Caffe::set_random_seed( 8 solver_->param().random_seed() + solver_->param().device_id()); 9 } 10 solver_->Step(solver_->param().max_iter() - initial_iter_); 11 }
GPU1调用Step()函数,进入迭代过程,见如下源码:
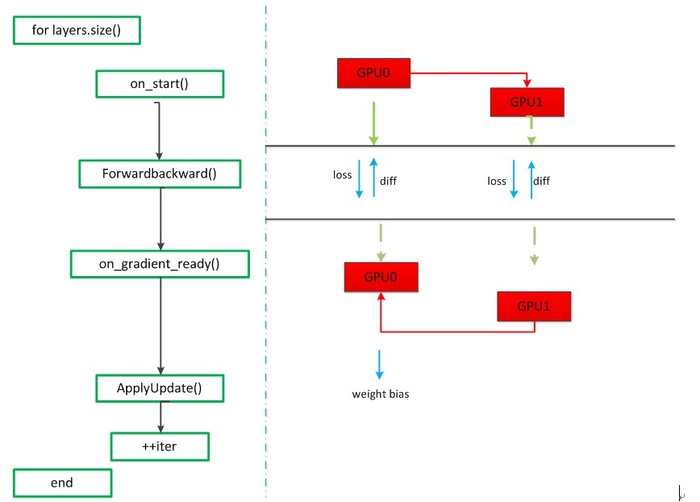
1 void Solver<Dtype>::Step(int iters) { 2 . . . . . . . . . . 3 while (iter_ < stop_iter) { 4 . . . . . . . . . . 5 for (int i = 0; i < callbacks_.size(); ++i) { 6 0_[i]->on_start(); 7 } 8 const bool display = param_.display() && iter_ % param_.display() == 0; 9 net_->set_debug_info(display && param_.debug_info()); 10 // accumulate the loss and gradient 11 Dtype loss = 0; 12 for (int i = 0; i < param_.iter_size(); ++i) { 13 loss += net_->ForwardBackward(bottom_vec);//计算loss,一次前后向 14 } 15 loss /= param_.iter_size();//loss归一化 16 . . . . . . . 17 for (int i = 0; i < callbacks_.size(); ++i) { 18 callbacks_[i]->on_gradients_ready(); 19 } 20 ApplyUpdate(); 21 . . . . . . . . . . 22 ++iter_; 23 } 24 }
整个Step函数的运行如上所示,首先根GPU(GPU0)有整个网络的网络参数,callbacks_.size()指的是GPU树的parent的个数(在这里是1),on_start()函数的作用就是把根GPU(GPU0)的网络参数分发到每一个子GPU(GPU1),GPU1会先进入这个函数,on_start()函数的部分代码如下:
1 void P2PSync<Dtype>::on_start() { 2 . . . . . . . 3 // Wait for update from parent 4 if (parent_) { 5 P2PSync<Dtype> *parent = queue_.pop();//取队列中的第一个gpu节点为根gpu 6 CHECK(parent == parent_); 7 } 8 . . . . . .
当执行到queue_.pop()时,会调用blocking_queue.cpp的pop()方法,pop()方法的内容如下:
1 T BlockingQueue<T>::pop(const string& log_on_wait) { 2 boost::mutex::scoped_lock lock(sync_->mutex_); 3 while (queue_.empty()) { 4 if (!log_on_wait.empty()) { 5 LOG_EVERY_N(INFO, 1000)<< log_on_wait; 6 } 7 sync_->condition_.wait(lock);//如果queue_为空,就一直阻塞。 8 }
该方法内部有wait()函数,因为此时queue_为空,所以GPU1就会被堵塞,因为GPU0和GPU1是两个线程并行运行,所以GPU0会执行run()函数中的下一步,也就是solver_->Solve(),Solve()函数的代码如下:
1 void Solver<Dtype>::Solve(const char* resume_file) { 2 int start_iter = iter_; 3 . . . . . 4 //LOG(INFO) <<"This is the sign of the train begin?********Ni****Jian*********"; //test for nijian 5 Step(param_.max_iter() - iter_); 6 . . . . . 7 }
Solve()函数会调用Step()函数进入迭代过程,当GPU0进入on_start()函数后,会把队列中的GPU0出队列,同时会激活被堵塞的GPU1,接下来的on_start()函数代码如下:
1 . . . . . 2 // Update children 3 for (int i = children_.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 4 Dtype* src = data_; 5 Dtype* dst = children_[i]->data_; 6 #ifdef DEBUG 7 . . . . 8 #endif 9 CUDA_CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(dst, src, size_ * sizeof(Dtype), 10 cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice, cudaStreamDefault));//每个子GPU把信息传入到根GPU,异步操作 11 CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(cudaStreamDefault));//根GPU把信息同步传到各个子GPU 12 children_[i]->queue_.push(this); 13 } 14 #endif 15 }
在该部分代码中,src指的是GPU0的data(网络参数),dst指的是GPU1的data(网络参数),通过调用cudaMemcpyAsync()函数来放置一个请求,表示在cudaStreamDefault流中执行一次内存复制操作,然后调用cudaStreamSynchronize()等待cudaStreamDefault流中的操作完成后实现流的同步。经过这两个函数后,GPU0完成了把网络参数分发给GPU1,然后children_[i]->queue_.push(this)被执行后,会调用block_queue.cpp文件中的push函数激活GPU0的子GPU,即GPU1,同时把GPU1压入队列,此时队列中只有GPU1。
1 void BlockingQueue<T>::push(const T& t) { 2 boost::mutex::scoped_lock lock(sync_->mutex_); 3 queue_.push(t); 4 lock.unlock(); 5 sync_->condition_.notify_one(); 6 }
此时,多个GPU的参数分发过程已经完成,接下来GPU0和GPU1并行执行Step()函数的下一步,即:ForwardBackward(),该函数的代码如下:
1 Dtype ForwardBackward(const vector<Blob<Dtype>* > & bottom) { 2 Dtype loss; 3 Forward(bottom, &loss); 4 Backward(); 5 return loss; 6 }
该函数的主要作用就是就是计算出loss和梯度diff,然后再接着执行Step()函数中的下一步,即:on_gradients_ready()函数,该函数分为两个部分,第一部分是多个GPU的梯度加和,第二部分是将计算后的梯度传给根GPU(GPU0)。第一部分的代码如下:
1 void P2PSync<Dtype>::on_gradients_ready() {. . . . . . . . 2 // Sum children gradients as they appear in the queue 3 for (int i = 0; i < children_.size(); ++i) { 4 P2PSync<Dtype> *child = queue_.pop(); 5 Dtype* src = child->parent_grads_; 6 Dtype* dst = diff_; 7 #ifdef DEBUG 8 cudaPointerAttributes attributes; 9 CUDA_CHECK(cudaPointerGetAttributes(&attributes, src)); 10 CHECK(attributes.device == device); 11 CUDA_CHECK(cudaPointerGetAttributes(&attributes, dst)); 12 CHECK(attributes.device == device); 13 #endif 14 caffe_gpu_add(size_, src, dst, dst); 15 }
第一部分是多个GPU的梯度加和,因为GPU0和GPU1是并行计算的,如果GPU0执行到这里时,会使队列中仅有的GPU1出队列,然后通过调用caffe_gpu_add()函数,将一个GPU的梯度diff直接传给另一个GPU,不需要经过CPU通信,即GPU1把其计算的diff传给GPU0。如果是GPU1执行到这里时,因为GPU1没有子GPU,所以会直接跳过这一部分。第二部分的代码如下:
1 if (parent_) { 2 Dtype* src = diff_; 3 Dtype* dst = parent_grads_; 4 #ifdef DEBUG 5 #endif 6 CUDA_CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(dst, src, size_ * sizeof(Dtype), // 7 cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice, cudaStreamDefault)); 8 CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(cudaStreamDefault)); 9 parent_->queue_.push(this); 10 } else { 11 // Loss functions divide gradients by the batch size, so to compensate 12 // for split batch, the root solver divides by number of solvers. 13 caffe_gpu_scal(size_, Dtype(1.0 / Caffe::solver_count()), diff_); 14 }
如果是GPU0的话,会执行else,即caffe_gpu_scal(),该函数把得到的之前计算的梯度diff_和除以GPU的个数,来更新梯度。如果是GPU1的话,会执行if的语句,此时和on_start()函数分析类似,经过cudaMemcpyAsync()和cudaStreamSynchronize()函数操作之后,将GPU1中的梯度传送给GPU0,第二部分完成。
接下来根GPU(GPU0)会得到所有的参数信息,会执行Step()函数的下一步,即执行ApplyUpdate()函数,该函数中有一个程序:CHECK(Caffe::root_solver()),会在根GPU中利用梯度下降法更新权重,计算参数,到此为止一次迭代完成,再进入下一次迭代时,根GPU已经保存了所有的网络参数,再继续迭代循环,直至结束。
本站文章如无特殊说明,均为本站原创,如若转载,请注明出处:Caffe参数交换源码分析 - Python技术站

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫  支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫