LSTM 参数
input_size:输入维数 hidden_size:输出维数 num_layers:LSTM层数,默认是1 bias:True 或者 False,决定是否使用bias, False则b_h=0. 默认为True batch_first:True 或者 False,因为nn.lstm()接受的数据输入是(序列长度,batch,输入维数),这和我们cnn输入的方式不太一致,所以使用batch_first,我们可以将输入变成(batch,序列长度,输入维数) dropout:表示除了最后一层之外都引入一个dropout bidirectional:表示双向LSTM,也就是序列从左往右算一次,从右往左又算一次,这样就可以两倍的输出
输入
– input (seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
– h_0 (num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size)
– c_0 (num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size)
输出
– output (seq_len, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size)
– h_n (num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size)
– c_n (num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, hidden_size)
【注】如果batch_first = True,则output (batch_size, seq_len, num_directions * hidden_size),而h_n和c_n的维度不会改变
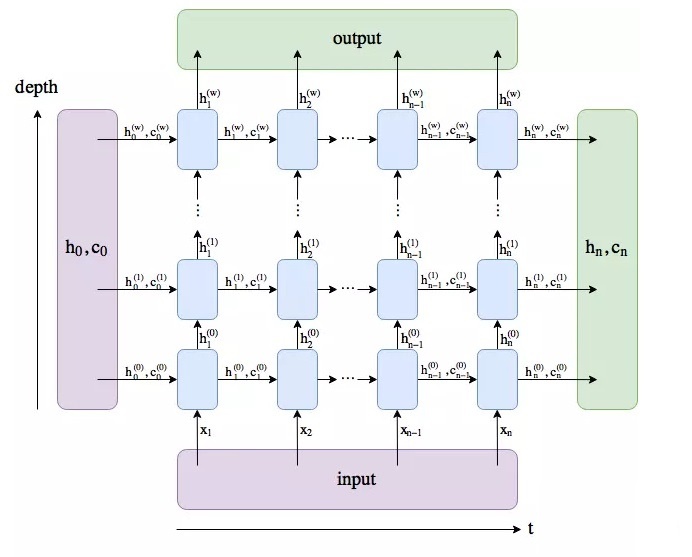
根据上面这张图可以分析LSTM返回的三个值 output、h_n 和 c_n 的维度:
— h_n:只返回最后一个时间步的隐藏层输出,第$i$层会输出$h_{n}^{(i)}$,所以第一维为num_layers * num_directions,第二维的维度为batch_size,第三位就是$h$本身的维度大小,即hidden_size。
— c_n:$c_n$的维度同$h_n$。
—output:返回每个时间步的隐藏层输出,所以第一维为seq_len,第二维的维度为batch_size,第三维就是hidden_size,双向的话拼接起来就是2*hidden_size,所以就是num_directions * hidden_size。
由于 h_n 和 output 都包含了最后一个时间步的隐藏层输出,所以$output[-1,:,:] = h_n[-1,:,:]$。
【注】如果batch_first=True,则 $output[:,-1,:] = h_n[-1,:,:]$
import torch import torch.nn as nn rnn = nn.LSTM(input_size=4, hidden_size=6, num_layers=1) input = torch.randn(3, 2, 4) # batch=2, seq_len=3, input_size=4 output, (hn, cn) = rnn(input) # 如果h0和c0未给出,则默认为0 print(output.shape, hn.shape, cn.shape) print(output[-1, :, :]) print(hn[-1, :, :])
参考:
【2】[深度学习] Pytorch中RNN/LSTM 模型小结
本站文章如无特殊说明,均为本站原创,如若转载,请注明出处:LSTM 的使用(Pytorch) - Python技术站



 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫  支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫