零、参考资料
有关FPN的介绍见『计算机视觉』FPN特征金字塔网络。
网络构架部分代码见Mask_RCNN/mrcnn/model.py中class MaskRCNN的build方法的"inference"分支。
1、Keras调用GPU设置
【*】指定GPU
import os os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "2"
【**】按需分配
import tensorflow as tf import keras.backend.tensorflow_backend as KTF config = tf.ConfigProto() config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True #不全部占满显存, 按需分配 # config.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.3 #指定分配30%空间 sess = tf.Session(config=config)# 设置session KTF.set_session(sess)
2、TensorFlow和Keras交互说明
下面的交互方法几乎都是对keras的函数式API操作的,不过keras的函数模型转换为model对象也极为方便,KM.Model(input_tensors, output_tensors)操作一下即可。
【*】使用TensorFlow建立keras新的层对象
在网络中我们可以看到大量的继承了keras.engine.Layer类的新类,这是因为如果TensorFlow函数可以操作keras的tensor,但是其返回的TensorFlow的tensor不能被keras继续处理,所以我们需要建立新的keras层进行转换,将tf的Tensor可作为keras层的__init__参数参与层构建,在__call__方法内部使用tf的函数进行细粒度数据处理,最后返回的是keras层对象。如果不想使用Model类的各种方便方法而执意手动使用tf.Session()训练的话就没有封装它们的必要了。
keras的tensor可以直接送入TensorFlow中:
import tensorflow as tf import keras.backend as K rpn_match = tf.placeholder(tf.int8, [10, 2]) tf.where(K.equal(rpn_match, 1))
一个class实现例子如下,注意需要推断输出的shape:
class PyramidROIAlign(KE.Layer):
"""Implements ROI Pooling on multiple levels of the feature pyramid.
Params:
- pool_shape: [pool_height, pool_width] of the output pooled regions. Usually [7, 7]
Inputs:
- boxes: [batch, num_boxes, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized
coordinates. Possibly padded with zeros if not enough
boxes to fill the array.
- image_meta: [batch, (meta data)] Image details. See compose_image_meta()
- feature_maps: List of feature maps from different levels of the pyramid.
Each is [batch, height, width, channels]
Output:
Pooled regions in the shape: [batch, num_boxes, pool_height, pool_width, channels].
The width and height are those specific in the pool_shape in the layer
constructor.
"""
def __init__(self, pool_shape, **kwargs):
super(PyramidROIAlign, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.pool_shape = tuple(pool_shape)
def call(self, inputs):
# num_boxes指的是proposal数目,它们均会作用于每张图片上,只是不同的proposal作用于图片
# 的特征级别不同,我通过循环特征层寻找符合的proposal,应用ROIAlign
# Crop boxes [batch, num_boxes, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coords
boxes = inputs[0]
# Image meta
# Holds details about the image. See compose_image_meta()
image_meta = inputs[1]
# Feature Maps. List of feature maps from different level of the
# feature pyramid. Each is [batch, height, width, channels]
feature_maps = inputs[2:]
# Assign each ROI to a level in the pyramid based on the ROI area.
y1, x1, y2, x2 = tf.split(boxes, 4, axis=2)
h = y2 - y1
w = x2 - x1
# Use shape of first image. Images in a batch must have the same size.
image_shape = parse_image_meta_graph(image_meta)['image_shape'][0] # h, w, c
# Equation 1 in the Feature Pyramid Networks paper. Account for
# the fact that our coordinates are normalized here.
# e.g. a 224x224 ROI (in pixels) maps to P4
image_area = tf.cast(image_shape[0] * image_shape[1], tf.float32)
roi_level = log2_graph(tf.sqrt(h * w) / (224.0 / tf.sqrt(image_area))) # h、w已经归一化
roi_level = tf.minimum(5, tf.maximum(
2, 4 + tf.cast(tf.round(roi_level), tf.int32))) # 确保值位于2到5之间
roi_level = tf.squeeze(roi_level, 2) # [batch, num_boxes]
# Loop through levels and apply ROI pooling to each. P2 to P5.
pooled = []
box_to_level = []
for i, level in enumerate(range(2, 6)):
# tf.where 返回值格式 [坐标1, 坐标2……]
# np.where 返回值格式 [[坐标1.x, 坐标2.x……], [坐标1.y, 坐标2.y……]]
ix = tf.where(tf.equal(roi_level, level)) # 返回坐标表示:第n张图片的第i个proposal
level_boxes = tf.gather_nd(boxes, ix) # [本level的proposal数目, 4]
# Box indices for crop_and_resize.
box_indices = tf.cast(ix[:, 0], tf.int32) # 记录每个propose对应图片序号
# Keep track of which box is mapped to which level
box_to_level.append(ix)
# Stop gradient propogation to ROI proposals
level_boxes = tf.stop_gradient(level_boxes)
box_indices = tf.stop_gradient(box_indices)
# Crop and Resize
# From Mask R-CNN paper: "We sample four regular locations, so
# that we can evaluate either max or average pooling. In fact,
# interpolating only a single value at each bin center (without
# pooling) is nearly as effective."
#
# Here we use the simplified approach of a single value per bin,
# which is how it's done in tf.crop_and_resize()
# Result: [this_level_num_boxes, pool_height, pool_width, channels]
pooled.append(tf.image.crop_and_resize(
feature_maps[i], level_boxes, box_indices, self.pool_shape,
method="bilinear"))
# 输入参数shape:
# [batch, image_height, image_width, channels]
# [this_level_num_boxes, 4]
# [this_level_num_boxes]
# [height, pool_width]
# Pack pooled features into one tensor
pooled = tf.concat(pooled, axis=0) # [batch*num_boxes, pool_height, pool_width, channels]
# Pack box_to_level mapping into one array and add another
# column representing the order of pooled boxes
box_to_level = tf.concat(box_to_level, axis=0) # [batch*num_boxes, 2]
box_range = tf.expand_dims(tf.range(tf.shape(box_to_level)[0]), 1) # [batch*num_boxes, 1]
box_to_level = tf.concat([tf.cast(box_to_level, tf.int32), box_range],
axis=1) # [batch*num_boxes, 3]
# 截止到目前,我们获取了记录全部ROIAlign结果feat集合的张量pooled,和记录这些feat相关信息的张量box_to_level,
# 由于提取方法的原因,此时的feat并不是按照原始顺序排序(先按batch然后按box index排序),下面我们设法将之恢复顺
# 序(ROIAlign作用于对应图片的对应proposal生成feat)
# Rearrange pooled features to match the order of the original boxes
# Sort box_to_level by batch then box index
# TF doesn't have a way to sort by two columns, so merge them and sort.
# box_to_level[i, 0]表示的是当前feat隶属的图片索引,box_to_level[i, 1]表示的是其box序号
sorting_tensor = box_to_level[:, 0] * 100000 + box_to_level[:, 1] # [batch*num_boxes]
ix = tf.nn.top_k(sorting_tensor, k=tf.shape(
box_to_level)[0]).indices[::-1]
ix = tf.gather(box_to_level[:, 2], ix)
pooled = tf.gather(pooled, ix)
# Re-add the batch dimension
# [batch, num_boxes, (y1, x1, y2, x2)], [batch*num_boxes, pool_height, pool_width, channels]
shape = tf.concat([tf.shape(boxes)[:2], tf.shape(pooled)[1:]], axis=0)
pooled = tf.reshape(pooled, shape)
return pooled # [batch, num_boxes, pool_height, pool_width, channels]
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return input_shape[0][:2] + self.pool_shape + (input_shape[2][-1], )
【**】keras的Lambda函数可以直接将TensorFlow操作引入keras
keras的Module不能接收tf的tensor作为数据流,所有需要使用KL.Lambda将之转化为keras的数据流,如下这样将tf写好的函数输出直接转换为keras的Module可以接收的类型,和上面的方法1相比,这里的lambda接受外部参数(一般位于类的__inti__中)调整函数行为并不方便:
rpn_bbox = KL.Lambda(lambda t: tf.reshape(t, [tf.shape(t)[0], -1, 4]))(x)
【***】继承keras.layer的层对象
和方法1相比,这种方法同样需要实现__call__方法,不过一般会super父类,用于改写keras已经实现的层方法。
class BatchNorm(KL.BatchNormalization):
"""Extends the Keras BatchNormalization class to allow a central place
to make changes if needed.
Batch normalization has a negative effect on training if batches are small
so this layer is often frozen (via setting in Config class) and functions
as linear layer.
"""
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
"""
Note about training values:
None: Train BN layers. This is the normal mode
False: Freeze BN layers. Good when batch size is small
True: (don't use). Set layer in training mode even when making inferences
"""
return super(self.__class__, self).call(inputs, training=training)
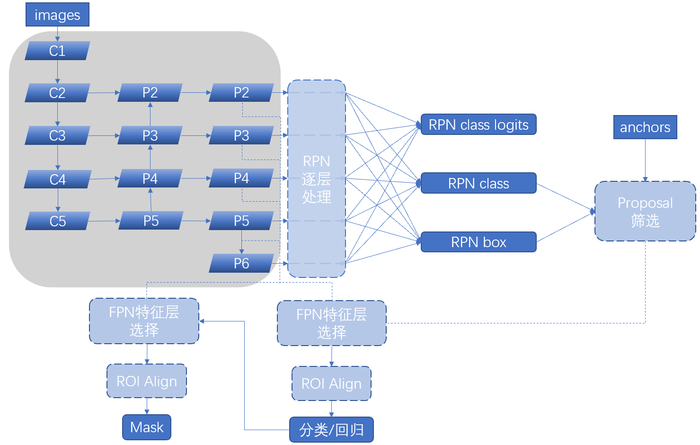
一、共享网络概览
按照逻辑顺序,我们首先来看处于流程图左上角的整张图最大的组成分支:特征提取网络。
可以看到本部分大致分为以下几个部分(即原图的三列):
ResNet101部分(FPN的bottom-up部分)
FPN的up-bottom部分和横向连接部分
最终特征重构部分
二、源码浏览
整个MaskRCNN类初始化之后的第一个方法就是build网络用的,在mode参数为inference情况下,下面给出了正式建立特征提取网络之前的class内部前置代码,
class MaskRCNN():
"""Encapsulates the Mask RCNN model functionality.
The actual Keras model is in the keras_model property.
"""
def __init__(self, mode, config, model_dir):
"""
mode: Either "training" or "inference"
config: A Sub-class of the Config class
model_dir: Directory to save training logs and trained weights
"""
assert mode in ['training', 'inference']
self.mode = mode
self.config = config
self.model_dir = model_dir
self.set_log_dir()
self.keras_model = self.build(mode=mode, config=config)
def build(self, mode, config):
"""Build Mask R-CNN architecture.
input_shape: The shape of the input image.
mode: Either "training" or "inference". The inputs and
outputs of the model differ accordingly.
"""
assert mode in ['training', 'inference']
# Image size must be dividable by 2 multiple times
h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2] # [1024 1024 3]
if h / 2**6 != int(h / 2**6) or w / 2**6 != int(w / 2**6):
raise Exception("Image size must be dividable by 2 at least 6 times "
"to avoid fractions when downscaling and upscaling." # <-----
"For example, use 256, 320, 384, 448, 512, ... etc. ")
# Inputs
input_image = KL.Input(
shape=[None, None, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[2]], name="input_image")
input_image_meta = KL.Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_META_SIZE],
name="input_image_meta")
if mode == "training":
……
elif mode == "inference":
# Anchors in normalized coordinates
input_anchors = KL.Input(shape=[None, 4], name="input_anchors")
这里强制要求了图片裁剪后尺度为2^n,且n>=6,保证下采样后不产生小数
整个程序需要外部输入的变量(inference模式)仅有三个,注意keras的习惯不同于placeholder,上面代码的shape没有包含batch,实际shape是下面的样式:
input_image:输入图片,[batch, None, None, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[2]]
input_image_meta:图片的信息(包含形状、预处理信息等,后面会介绍),[batch, config.IMAGE_META_SIZE]
input_anchors:锚框,[batch, None, 4]
ResNet101部分
接上面build函数代码,经由如下判断(inference中该参数是字符串"resnet101",所以进入else分支),建立ResNet网络图,
# Build the shared convolutional layers.
# Bottom-up Layers
# Returns a list of the last layers of each stage, 5 in total.
# Don't create the thead (stage 5), so we pick the 4th item in the list.
if callable(config.BACKBONE):
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = config.BACKBONE(input_image, stage5=True,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
else:
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = resnet_graph(input_image, config.BACKBONE,
stage5=True, train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
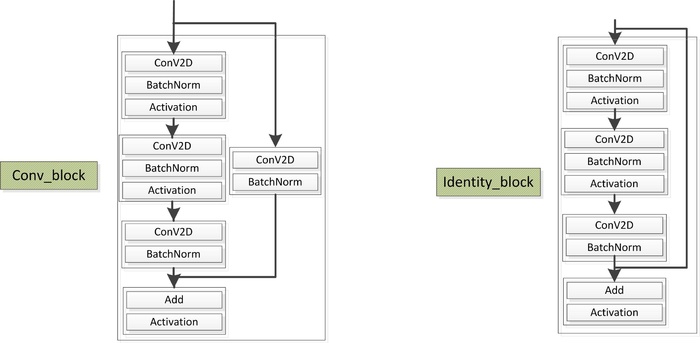
上述主函数调用ResNet图构建代码如下,其包含应用shortcut和没有应用shortcut两种子结构:
(图摘自网上)
############################################################
# Resnet Graph
############################################################
# Code adopted from:
# https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/blob/master/resnet50.py
def identity_block(input_tensor, kernel_size, filters, stage, block,
use_bias=True, train_bn=True):
"""The identity_block is the block that has no conv layer at shortcut
# Arguments
input_tensor: input tensor
kernel_size: default 3, the kernel size of middle conv layer at main path
filters: list of integers, the nb_filters of 3 conv layer at main path
stage: integer, current stage label, used for generating layer names
block: 'a','b'..., current block label, used for generating layer names
use_bias: Boolean. To use or not use a bias in conv layers.
train_bn: Boolean. Train or freeze Batch Norm layers
"""
nb_filter1, nb_filter2, nb_filter3 = filters
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
x = KL.Conv2D(nb_filter1, (1, 1), name=conv_name_base + '2a',
use_bias=use_bias)(input_tensor)
x = BatchNorm(name=bn_name_base + '2a')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
x = KL.Conv2D(nb_filter2, (kernel_size, kernel_size), padding='same',
name=conv_name_base + '2b', use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNorm(name=bn_name_base + '2b')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
x = KL.Conv2D(nb_filter3, (1, 1), name=conv_name_base + '2c',
use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNorm(name=bn_name_base + '2c')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Add()([x, input_tensor])
x = KL.Activation('relu', name='res' + str(stage) + block + '_out')(x)
return x
def conv_block(input_tensor, kernel_size, filters, stage, block,
strides=(2, 2), use_bias=True, train_bn=True):
"""conv_block is the block that has a conv layer at shortcut
# Arguments
input_tensor: input tensor
kernel_size: default 3, the kernel size of middle conv layer at main path
filters: list of integers, the nb_filters of 3 conv layer at main path
stage: integer, current stage label, used for generating layer names
block: 'a','b'..., current block label, used for generating layer names
use_bias: Boolean. To use or not use a bias in conv layers.
train_bn: Boolean. Train or freeze Batch Norm layers
Note that from stage 3, the first conv layer at main path is with subsample=(2,2)
And the shortcut should have subsample=(2,2) as well
"""
nb_filter1, nb_filter2, nb_filter3 = filters
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
x = KL.Conv2D(nb_filter1, (1, 1), strides=strides,
name=conv_name_base + '2a', use_bias=use_bias)(input_tensor)
x = BatchNorm(name=bn_name_base + '2a')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
x = KL.Conv2D(nb_filter2, (kernel_size, kernel_size), padding='same',
name=conv_name_base + '2b', use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNorm(name=bn_name_base + '2b')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
x = KL.Conv2D(nb_filter3, (1, 1), name=conv_name_base +
'2c', use_bias=use_bias)(x)
x = BatchNorm(name=bn_name_base + '2c')(x, training=train_bn)
shortcut = KL.Conv2D(nb_filter3, (1, 1), strides=strides,
name=conv_name_base + '1', use_bias=use_bias)(input_tensor)
shortcut = BatchNorm(name=bn_name_base + '1')(shortcut, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Add()([x, shortcut])
x = KL.Activation('relu', name='res' + str(stage) + block + '_out')(x)
return x
def resnet_graph(input_image, architecture, stage5=False, train_bn=True):
"""Build a ResNet graph.
architecture: Can be resnet50 or resnet101
stage5: Boolean. If False, stage5 of the network is not created
train_bn: Boolean. Train or freeze Batch Norm layers
"""
assert architecture in ["resnet50", "resnet101"]
# Stage 1
x = KL.ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(input_image)
x = KL.Conv2D(64, (7, 7), strides=(2, 2), name='conv1', use_bias=True)(x)
x = BatchNorm(name='bn_conv1')(x, training=train_bn)
x = KL.Activation('relu')(x)
C1 = x = KL.MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same")(x)
# Stage 2
x = conv_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='a', strides=(1, 1), train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b', train_bn=train_bn)
C2 = x = identity_block(x, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c', train_bn=train_bn)
# Stage 3
x = conv_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a', train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b', train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c', train_bn=train_bn)
C3 = x = identity_block(x, 3, [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d', train_bn=train_bn)
# Stage 4
x = conv_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a', train_bn=train_bn)
block_count = {"resnet50": 5, "resnet101": 22}[architecture]
for i in range(block_count):
x = identity_block(x, 3, [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block=chr(98 + i), train_bn=train_bn)
C4 = x
# Stage 5
if stage5:
x = conv_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a', train_bn=train_bn)
x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b', train_bn=train_bn)
C5 = x = identity_block(x, 3, [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c', train_bn=train_bn)
else:
C5 = None
return [C1, C2, C3, C4, C5]
BN层为了可能的扩展进行了封装,不过暂时没什么扩展:
class BatchNorm(KL.BatchNormalization):
"""Extends the Keras BatchNormalization class to allow a central place
to make changes if needed.
Batch normalization has a negative effect on training if batches are small
so this layer is often frozen (via setting in Config class) and functions
as linear layer.
"""
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
"""
Note about training values:
None: Train BN layers. This is the normal mode
False: Freeze BN layers. Good when batch size is small
True: (don't use). Set layer in training mode even when making inferences
"""
return super(self.__class__, self).call(inputs, training=training)
FPN处理部分
接上面build函数代码,剩下部分比较简单,和示意图对比几乎平铺直叙,
# Top-down Layers
# TODO: add assert to varify feature map sizes match what's in config
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5) # 256
P4 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p4add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)])
P3 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p3add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p4upsampled")(P4),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c3p3')(C3)])
P2 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p2add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p3upsampled")(P3),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c2p2')(C2)])
# Attach 3x3 conv to all P layers to get the final feature maps.
P2 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p2")(P2)
P3 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p3")(P3)
P4 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p4")(P4)
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p5")(P5)
# P6 is used for the 5th anchor scale in RPN. Generated by
# subsampling from P5 with stride of 2.
P6 = KL.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(1, 1), strides=2, name="fpn_p6")(P5)
接上面build函数代码,最后我们提取的特征集合如下:
# Note that P6 is used in RPN, but not in the classifier heads.
rpn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6]
mrcnn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5]
其中rpn_feature_maps对应图中的实线输出,送入RPN网络分类/回归得到锚框的前景/背景鉴别结果;而mrcnn_feature_maps则是后面进行ROI Align时的切割目标。
附录、build函数总览
def build(self, mode, config):
"""Build Mask R-CNN architecture.
input_shape: The shape of the input image.
mode: Either "training" or "inference". The inputs and
outputs of the model differ accordingly.
"""
assert mode in ['training', 'inference']
# Image size must be dividable by 2 multiple times
h, w = config.IMAGE_SHAPE[:2] # [1024 1024 3]
if h / 2**6 != int(h / 2**6) or w / 2**6 != int(w / 2**6): # 这里就限定了下采样不会产生坐标误差
raise Exception("Image size must be dividable by 2 at least 6 times "
"to avoid fractions when downscaling and upscaling."
"For example, use 256, 320, 384, 448, 512, ... etc. ")
# Inputs
input_image = KL.Input(
shape=[None, None, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[2]], name="input_image")
input_image_meta = KL.Input(shape=[config.IMAGE_META_SIZE],
name="input_image_meta")
if mode == "training":
# RPN GT
input_rpn_match = KL.Input(
shape=[None, 1], name="input_rpn_match", dtype=tf.int32)
input_rpn_bbox = KL.Input(
shape=[None, 4], name="input_rpn_bbox", dtype=tf.float32)
# Detection GT (class IDs, bounding boxes, and masks)
# 1. GT Class IDs (zero padded)
input_gt_class_ids = KL.Input(
shape=[None], name="input_gt_class_ids", dtype=tf.int32)
# 2. GT Boxes in pixels (zero padded)
# [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in image coordinates
input_gt_boxes = KL.Input(
shape=[None, 4], name="input_gt_boxes", dtype=tf.float32)
# Normalize coordinates
gt_boxes = KL.Lambda(lambda x: norm_boxes_graph(
x, K.shape(input_image)[1:3]))(input_gt_boxes)
# 3. GT Masks (zero padded)
# [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]
if config.USE_MINI_MASK:
input_gt_masks = KL.Input(
shape=[config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[0],
config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE[1], None],
name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool)
else:
input_gt_masks = KL.Input(
shape=[config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1], None],
name="input_gt_masks", dtype=bool)
elif mode == "inference":
# Anchors in normalized coordinates
input_anchors = KL.Input(shape=[None, 4], name="input_anchors")
# Build the shared convolutional layers.
# Bottom-up Layers
# Returns a list of the last layers of each stage, 5 in total.
# Don't create the thead (stage 5), so we pick the 4th item in the list.
if callable(config.BACKBONE):
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = config.BACKBONE(input_image, stage5=True,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
else:
_, C2, C3, C4, C5 = resnet_graph(input_image, config.BACKBONE,
stage5=True, train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# Top-down Layers
# TODO: add assert to varify feature map sizes match what's in config
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c5p5')(C5) # 256
P4 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p4add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p5upsampled")(P5),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c4p4')(C4)])
P3 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p3add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p4upsampled")(P4),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c3p3')(C3)])
P2 = KL.Add(name="fpn_p2add")([
KL.UpSampling2D(size=(2, 2), name="fpn_p3upsampled")(P3),
KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (1, 1), name='fpn_c2p2')(C2)])
# Attach 3x3 conv to all P layers to get the final feature maps.
P2 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p2")(P2)
P3 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p3")(P3)
P4 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p4")(P4)
P5 = KL.Conv2D(config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE, (3, 3), padding="SAME", name="fpn_p5")(P5)
# P6 is used for the 5th anchor scale in RPN. Generated by
# subsampling from P5 with stride of 2.
P6 = KL.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(1, 1), strides=2, name="fpn_p6")(P5)
# Note that P6 is used in RPN, but not in the classifier heads.
rpn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6]
mrcnn_feature_maps = [P2, P3, P4, P5]
# Anchors
if mode == "training":
anchors = self.get_anchors(config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
# Duplicate across the batch dimension because Keras requires it
# TODO: can this be optimized to avoid duplicating the anchors?
anchors = np.broadcast_to(anchors, (config.BATCH_SIZE,) + anchors.shape)
# A hack to get around Keras's bad support for constants
anchors = KL.Lambda(lambda x: tf.Variable(anchors), name="anchors")(input_image)
else:
anchors = input_anchors
# RPN Model, 返回的是keras的Module对象, 注意keras中的Module对象是可call的
rpn = build_rpn_model(config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE, # 1 3 256
len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS), config.TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE)
# Loop through pyramid layers
layer_outputs = [] # list of lists
for p in rpn_feature_maps:
layer_outputs.append(rpn([p])) # 保存各pyramid特征经过RPN之后的结果
# Concatenate layer outputs
# Convert from list of lists of level outputs to list of lists
# of outputs across levels.
# e.g. [[a1, b1, c1], [a2, b2, c2]] => [[a1, a2], [b1, b2], [c1, c2]]
output_names = ["rpn_class_logits", "rpn_class", "rpn_bbox"]
outputs = list(zip(*layer_outputs)) # [[logits2,……6], [class2,……6], [bbox2,……6]]
outputs = [KL.Concatenate(axis=1, name=n)(list(o))
for o, n in zip(outputs, output_names)]
# [batch, num_anchors, 2/4]
# 其中num_anchors指的是全部特征层上的anchors总数
rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox = outputs
# Generate proposals
# Proposals are [batch, N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates
# and zero padded.
# POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE = 1000
# POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING = 2000
proposal_count = config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING if mode == "training"\
else config.POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE
# [IMAGES_PER_GPU, num_rois, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
# IMAGES_PER_GPU取代了batch,之后说的batch都是IMAGES_PER_GPU
rpn_rois = ProposalLayer(
proposal_count=proposal_count,
nms_threshold=config.RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD, # 0.7
name="ROI",
config=config)([rpn_class, rpn_bbox, anchors])
if mode == "training":
# Class ID mask to mark class IDs supported by the dataset the image
# came from.
active_class_ids = KL.Lambda(
lambda x: parse_image_meta_graph(x)["active_class_ids"]
)(input_image_meta)
if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS:
# Ignore predicted ROIs and use ROIs provided as an input.
input_rois = KL.Input(shape=[config.POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING, 4],
name="input_roi", dtype=np.int32)
# Normalize coordinates
target_rois = KL.Lambda(lambda x: norm_boxes_graph(
x, K.shape(input_image)[1:3]))(input_rois)
else:
target_rois = rpn_rois
# Generate detection targets
# Subsamples proposals and generates target outputs for training
# Note that proposal class IDs, gt_boxes, and gt_masks are zero
# padded. Equally, returned rois and targets are zero padded.
rois, target_class_ids, target_bbox, target_mask =\
DetectionTargetLayer(config, name="proposal_targets")([
target_rois, input_gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, input_gt_masks])
# Network Heads
# TODO: verify that this handles zero padded ROIs
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\
fpn_classifier_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, input_image_meta,
config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN,
fc_layers_size=config.FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE)
mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(rois, mrcnn_feature_maps,
input_image_meta,
config.MASK_POOL_SIZE,
config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
# TODO: clean up (use tf.identify if necessary)
output_rois = KL.Lambda(lambda x: x * 1, name="output_rois")(rois)
# Losses
rpn_class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="rpn_class_loss")(
[input_rpn_match, rpn_class_logits])
rpn_bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: rpn_bbox_loss_graph(config, *x), name="rpn_bbox_loss")(
[input_rpn_bbox, input_rpn_match, rpn_bbox])
class_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_class_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_class_loss")(
[target_class_ids, mrcnn_class_logits, active_class_ids])
bbox_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_bbox_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_bbox_loss")(
[target_bbox, target_class_ids, mrcnn_bbox])
mask_loss = KL.Lambda(lambda x: mrcnn_mask_loss_graph(*x), name="mrcnn_mask_loss")(
[target_mask, target_class_ids, mrcnn_mask])
# Model
inputs = [input_image, input_image_meta,
input_rpn_match, input_rpn_bbox, input_gt_class_ids, input_gt_boxes, input_gt_masks]
if not config.USE_RPN_ROIS:
inputs.append(input_rois)
outputs = [rpn_class_logits, rpn_class, rpn_bbox,
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask,
rpn_rois, output_rois,
rpn_class_loss, rpn_bbox_loss, class_loss, bbox_loss, mask_loss]
model = KM.Model(inputs, outputs, name='mask_rcnn')
else:
# Network Heads
# Proposal classifier and BBox regressor heads
# output shapes:
# mrcnn_class_logits: [batch, num_rois, NUM_CLASSES] classifier logits (before softmax)
# mrcnn_class: [batch, num_rois, NUM_CLASSES] classifier probabilities
# mrcnn_bbox(deltas): [batch, num_rois, NUM_CLASSES, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))]
mrcnn_class_logits, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox =\
fpn_classifier_graph(rpn_rois, mrcnn_feature_maps, input_image_meta,
config.POOL_SIZE, config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN,
fc_layers_size=config.FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE)
# Detections
# output is [batch, num_detections, (y1, x1, y2, x2, class_id, score)] in
# normalized coordinates
detections = DetectionLayer(config, name="mrcnn_detection")(
[rpn_rois, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox, input_image_meta])
# Create masks for detections
detection_boxes = KL.Lambda(lambda x: x[..., :4])(detections)
mrcnn_mask = build_fpn_mask_graph(detection_boxes, mrcnn_feature_maps,
input_image_meta,
config.MASK_POOL_SIZE,
config.NUM_CLASSES,
train_bn=config.TRAIN_BN)
model = KM.Model([input_image, input_image_meta, input_anchors],
[detections, mrcnn_class, mrcnn_bbox,
mrcnn_mask, rpn_rois, rpn_class, rpn_bbox],
name='mask_rcnn')
# Add multi-GPU support.
if config.GPU_COUNT > 1:
from mrcnn.parallel_model import ParallelModel
model = ParallelModel(model, config.GPU_COUNT)
return model
本站文章如无特殊说明,均为本站原创,如若转载,请注明出处:『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其二:基于ReNet101的FPN共享网络暨TensorFlow和Keras交互简介 - Python技术站

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫  支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫